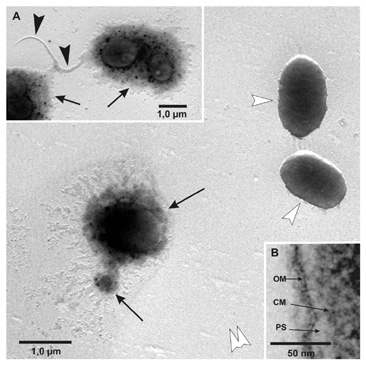
The Roseobacter lineage is one of the most abundant groups of bacteria in the world`s oceans and plays an important role for the global carbon and sulfur cycle; Dinoroseobacter shibae was isolated from toxic marine dinoflagellates and is able to perform aerobic anoxygenic photosynthesis, harbours seven linear plasmids which together comprise 861 kb of extrachromosomal information, and produces highly unusual quorum sensing signalling compounds, i.e. acylated homoserine lactones with side chain lengths of 18 carbon atoms, the longest AHL side chain length presently known. It is relevant to the Genomics-DTL program which supports systems microbiology, and to the Ocean Sciences Program which supports research to understand the ocean carbon cycle.
|
||
|
||
Dinoroseobacter shibae DFL-12, DSM 16493